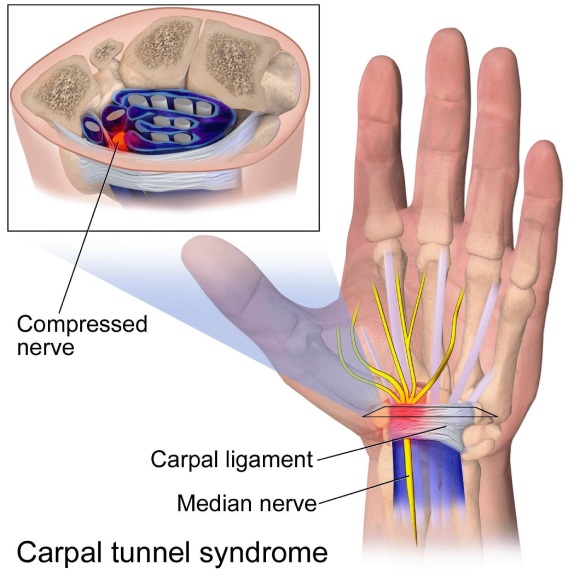
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome describes the condition where Compression the median nerve in an area of your wrist termed the ‘Carpal Tunnel‘ causes a painful burning sensation in the palm of your hand with tingling and numbness of the fingertips.
Often the patient experiences pins and needles in the thumb, index, middle and radial side of the ring finger.
The patient may get up several times during the night to vigorously shake their hands to ease the symptoms.
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome include:
- Pain in The hand
- Numbness in the hand
- Pins and needles or tingling in the hand/fingers
- A loss of power in your hand or dropping objects or a reduction in manual dexterity and precision of the hand/fingers
- Wasting of Hand Muscles on the Palm

These symptoms often occur at night and you may find they are often relieved by shaking your wrist vigorously for 15 to 30 seconds, providing temporary pain relief.
You may find that your symptoms are worse when you fall asleep. Your sleep may even be disturbed by the pain and pins and needles causing you to wake and shake your hands vigorously to ease the symptoms
When you wake up in the morning you may still have numbness and tingling in your hands that spreads all the way up to the forearms and to the shoulder.
In the daytime your symptoms may flare when you are bending your wrist during driving or working at a keyboard or vibrating machinery.
As carpal tunnel syndrome gets progressively worse you will notice a weakness in grip strength, more pain and your forearm muscles cramping.
Symptoms
Carpal tunnel syndrome can cause a range of symptoms, including:
Numbness, tingling, and burning sensations in the thumb, index, middle, and part of the ring finger
Weakness and clumsiness in the hands
Dropping objects due to numbness, or weakness
Tingling or pain in the forearm that radiates up to the shoulder
Shock-like feelings in the fingers
Pain or discomfort in the wrist or hand, especially at night
These symptoms can be caused by compression of the Median Nerve in the Carpal tunnel, which can be triggered by a variety of factors, including repetitive wrist movements, swelling of the tendons, and inflammatory conditions. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical advice to prevent further complications and to treat carpal tunnel syndrome effectively.
How is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome diagnosed?
Carpal tunnel syndrome is usually diagnosed from a careful history and examination.
The neck, shoulder and elbow are also examined to make sure the nerve compression is not occurring in a different region.
The median nerve compression test is a very useful test. To perform this test the clinician taps or applies pressure on the area where the median nerve is located to replicate the symptoms the patient experiences. If the symptoms are replicated it is a positive test. This is the Tinel’s Sign.
Another test is the Phalens test. Here the patient flexes the wrist in a ‘reverse prayer’ manoeuvre. Again replication of symptoms of pain and pins and needles in the medican nerve distribution is a positive sign.
Conditions such as pronator syndrome or a prolapsed disc affecting the C6 nerve in the neck region can present as carpal tunnel syndrome so an in-depth examination is essential
You may undergo nerve conduction studies but even in approximately 5-10% of cases, Carpal Tunnel syndrome these may be normal. They are however positive in the vast majority of cases.
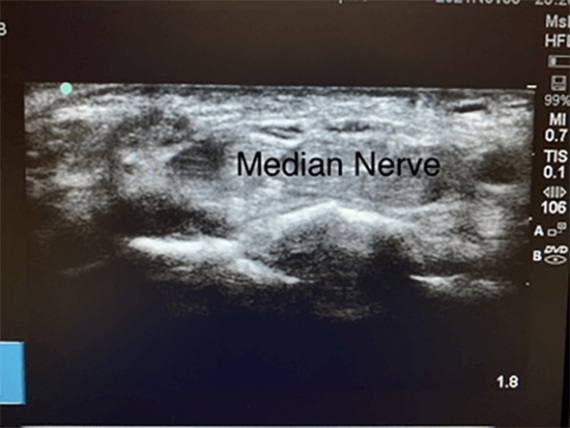
Here at MyMSK clinic we also use an ultrasound scanning machine to help make an accurate diagnosis.
Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is caused by any factor which causes compression or swelling of the median nerve at the wrist or causes narrowing of the carpal tunnel. There are several causes of carpal tunnel syndrome.
Often no single cause of carpal tunnel is is identified and it may be due to a combination of factors.
Risk factors
A narrow carpal tunnel can make a person more likely to have carpal tunnel syndrome. Anything that narrows the carpal tunnel i.e fracture or arthritis which may alter the small bones in the wrist may reduce the space within the carpal tunnel and therefore put pressure on the median nerve.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is more common in females especially between the ages of 40-60. One of the reasons for this is because the actual carpal tunnel area is relatively smaller in women than in men
Conditions such as Rheumatoid Arthritis or Tenosynovitis which have an inflammatory component can cause the tendons in your wrist to swell and therefore put pressure on the median nerve.
Conditions such as diabetes or thyroid issues may increase the risk of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. In addition conditions such as Menopause, Kidney failure and Lymphoedema may also increase the chances of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
High body mass index is a risk factor for carpal tunnel syndrome.
When the body retains fluid such as in pregnancy and in menopause this increases the pressure within the carpal tunnel which also irritates the median nerve. In pregnancy carpal tunnel syndrome tends to get better after delivery.
Working in an occupation that requires repetitive and prolonged wrist flexion may contribute towards carpal tunnel syndrome. Occupations where power tools are used and extensively computer use especially when working with the mouse may also be risk factor.
Prevention
While carpal tunnel syndrome cannot be completely prevented, there are several steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing the condition:
Reduce force and relax grip when performing activities
Take short, frequent breaks to stretch hands and wrists
Change tasks whenever possible
Use proper posture and keep the keyboard at or just below elbow height
Use a large pen with a large, comfortable grip adapter and free-flowing ink
Keep hands warm in cold workplaces
Avoid bending or twisting the wrist, especially when performing repetitive tasks
Take regular breaks to stretch and move around
By taking these steps, individuals can reduce their risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome and alleviate symptoms if they do occur. Implementing ergonomic practices and making small adjustments to daily activities can make a significant difference in preventing carpal tunnel syndrome.
Treatment of Carpal Tunnel syndrome
Although Carpal Tunnel Syndrome often comes on gradually, it is important to treat it early to prevent long term disability and potentially irreversible muscle damage.
If diagnosed and treated early when the symptoms may be mild, surgery may be avoided.
A non surgical approach is recommended initially:

-
Wrist splint: Wrist splint: Wearing a splint at night works by preventing flexion of the wrist. This in turn reduces the pressure on the median nerve in the carpal tunnel. It may also be useful to wear the Splint during the day when doing activities which may bring on carpal tunnel syndrome.
-
NSAIDS: Non-Steroidal Anti Inflammatory Medications i.e Ibuprofen or Naproxen often these can help relieve pain and inflammation.
- Nerve flossing exercises: Occasionally patients may benefit from specific exercises that help the median nerve glide more freely within the carpal tunnel.
- Activity modification: This involves being able to identify certain activities or wrist movements in your job or hobby which make carpal tunnel syndrome worse. Altering or modifying these can help slow or stop the progression. You may need ergonomic input to alter things such as the workstation setup or tools being used at work if you work with machinery.
- Cortisone injection: These are powerful anti inflammatory medications that can be directed into the carpal tunnel. These injections can often relieve painful symptoms and help to control flare ups. A good response to the injection also helps your doctor in diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome.
We here at MyMSK clinic tend to use an Ultrasound guided injection to help release or create for the median nerve.
An ultrasound-guided injection really adds precision to the procedure and makes a successful outcome more likely. It also helps avoid complications such as damage to the median nerve. Sometimes more than one injection is required to adequately control symptoms. It is crucial to consult qualified physicians based on their training, certification, and treatment proficiency to ensure the best care.
Carpal Tunnel Injection Manchester
The Injection procedure performed for carpal tunnel syndrome is termed Carpal Tunnel Hydrodissection.
Often Carpal tunnel injections are done as an outpatient procedure under local Anaesthesia.
The procedure involves injection under the ligament that forms the roof of the tunnel. This ligament is called a flexor retinaculum. By performing a hydrodissection of the nerve under this ligament, the aim is to relieve the pressure within the carpal tunnel and an easing of symptoms.
What to Expect During the Carpal Tunnel Hydrodissection
Hydrodissection for carpal tunnel syndrome is typically performed as an outpatient procedure under local anesthesia.
The procedure involves carefully hydrodissecting the median nerve from the ligament that forms the roof of the tunnel, known as the transverse carpal ligament, to relieve pressure on the median nerve.
During the procedure, the Physician will:
Place a numbing injection on the wrist
Hydrodissect under the transverse carpal ligament to relieve pressure on the median nerve
Apply a dressing over the area once the procedure is completed
The procedure typically takes about 15-30 minutes to complete, and patients can usually return home the same day. After the procedure, patients may experience some pain, swelling, and bruising, but these symptoms can be managed with pain medication and ice. It is important to follow the Doctor’s post-operative instructions to ensure a smooth recovery and to prevent complications.
When the symptoms are longstanding and the muscles of the hand are also affected, surgery may be recommended to prevent irreversible damage.
If you feel you may be having a medical emergency please contact 999 or your doctor immediately.
If you have any Health related concerns please contact a qualified physician/doctor as soon as possible.
Alternative to Surgery
For some patients, the Hydrodissection may not be the best option for treating carpal tunnel syndrome. In these cases, alternative treatments may be recommended, such as:t
Physical therapy: This can help to improve wrist mobility and strength, reduce pain and inflammation, and promote healing.
Wrist splints: These can be worn to immobilize the wrist and reduce pressure on the median nerve.
Lifestyle modifications: Making changes to daily activities and habits, such as taking regular breaks to stretch and move around, can help to alleviate symptoms and prevent further injury.
These alternatives can be effective in managing carpal tunnel syndrome, especially when combined with early diagnosis and treatment.
Consulting with a clinician can help determine the best course of action based on individual needs and circumstances.
Post Carpal Tunnel Injection-Recovery and Rehabilitation
After the procedure or alternative treatment, patients will need to undergo a period of recovery and rehabilitation to ensure proper healing and prevent further injury.
Immediately after the procedure, patients should:- Elevate the affected hand above the level of the heart to reduce swelling
Apply ice to the affected area to reduce pain and inflammation
Take pain medication as directed by the Doctor
In the days and weeks following procedure, patients should:- Gradually increase activity levels, starting with gentle exercises and gradually increasing intensity and duration
Avoid heavy lifting, bending, or twisting
Wear a wrist splint to immobilize the wrist and reduce pressure on the median nerve
Physical therapy may be recommended to promote healing, improve wrist mobility and strength, and reduce pain and inflammation.
By following these steps, patients can ensure a smooth and successful recovery from carpal tunnel syndrome treatment. It is important to adhere to the rehabilitation plan provided by healthcare professionals to achieve the best possible outcomes.
Contact us
We’d love to hear from you!
Just reach out and contact us via any of
these channels:

Call us on

Email us on

Call us on

