Osteopath doctor
What is an Osteopath?
An Osteopath Doctor is a manual therapy practitioner who offers treatment focusing on muscles, soft tissues and joints.
Osteopaths utilise a holistic approach, aiming to improve the body’s overall healing system.
An Osteopath attempts to diagnose conditions with their palpatory skills which are honed through years of practice.
Painful conditions are then treated with a range of techniques including soft tissue mobilisation and manipulations of bones and muscles.
In turn, this therapy helps in relieving pain in joints and muscles that may cause referred pain.
Osteopaths can treat a number of conditions such as soft tissue injury, back pain, joint pain, slipped disc and trapped nerves.
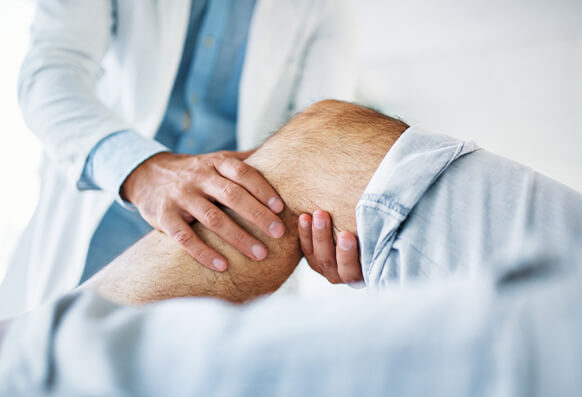
Although osteopaths use a range of gentle techniques and often focus on mobilisation therapy to help ease your aches and pains, It is not uncommon to continue feeling the symptoms right after an osteopathic treatment, and in some cases even feel more sore and tired for 24-48 hour after treatment.
This is often because the body tissue biomechanics have often been re-set and it takes for the body to adjust to a new biomechanical setting.
In the UK, an osteopath is a healthcare professional who specializes in diagnosing, treating, and preventing a range of health problems through manual therapy, lifestyle advice, and exercise. Here’s a detailed look at the role and practice of osteopaths in the UK:
Education and Training
- Degree Program: To become an osteopath in the UK, individuals must complete an undergraduate or postgraduate degree in osteopathy, which typically lasts four to five years. These programs are rigorous and cover subjects such as anatomy, physiology, pathology, and osteopathic techniques.
- Accreditation: Osteopathic degree programs in the UK are accredited by the General Osteopathic Council (GOsC), the regulatory body for osteopathy in the UK.
Regulatory Body
- General Osteopathic Council (GOsC): All practicing osteopaths in the UK must be registered with the GOsC. The GOsC sets and maintains standards of osteopathic practice and conduct, ensuring that osteopaths are competent and safe practitioners.
- Continuing Professional Development (CPD): Registered osteopaths are required to undertake CPD to keep their knowledge and skills up-to-date.
Scope of Practice
- Manual Therapy: Osteopaths use hands-on techniques to treat musculoskeletal issues, such as back pain, neck pain, joint pain, and muscle strains. Techniques may include stretching, massaging, and mobilizing joints.
- Holistic Approach: Osteopaths in the UK take a holistic approach, considering the patient’s lifestyle, activities, and overall health in their treatments. They aim to improve the function of the body’s musculoskeletal system as well as overall health and wellbeing.
- Patient Advice: They often provide advice on posture, exercise, diet, and ergonomics to help prevent further problems.
- No Prescribing Rights: Unlike in some other countries, osteopaths in the UK do not prescribe medication or perform surgery.
Differences from Other Healthcare Professionals
- Versus Physiotherapists: While both physiotherapists and osteopaths treat musculoskeletal problems, osteopaths are more likely to use a holistic and hands-on approach involving the whole body.
- Versus Chiropractors: Osteopaths treat a wider range of conditions and use a broader set of techniques compared to chiropractors, who primarily focus on the spine and joint adjustments.
Regulation and Standards
- Protection of Title: The title “osteopath” is protected by law in the UK, meaning only those registered with the GOsC can legally practice as osteopaths.
- Professional Standards: Osteopaths must adhere to the standards of practice and conduct set by the GOsC, which include maintaining high levels of professional competence and conduct.
Choosing an Osteopath
- Consultation: When choosing an osteopath, it is advisable to check their registration with the GOsC, ensuring they meet the required standards of practice.
- Referrals and Recommendations: Many people are referred to osteopaths by their GPs or find them through personal recommendations.
Osteopaths in the UK play a key role in managing and treating musculoskeletal conditions through a holistic, patient-centered approach. Their emphasis on manual therapy and lifestyle advice helps support overall health and wellbeing.