Sesamoiditis and Gout are two conditions that can cause pain in the big toe.
It can be difficult to tell the difference between the two, as the symptoms can be similar.
However, there are be some differences between the two conditions that can help with identification and diagnosis.
Sesamoiditis is a condition that affects the sesamoid bones in the foot. These are two small bones that are located under the big toe joint.
Sesamoiditis can be caused by overuse, injury or degeneration in these bones, and can result in pain, swelling, and difficulty in moving the big toe.
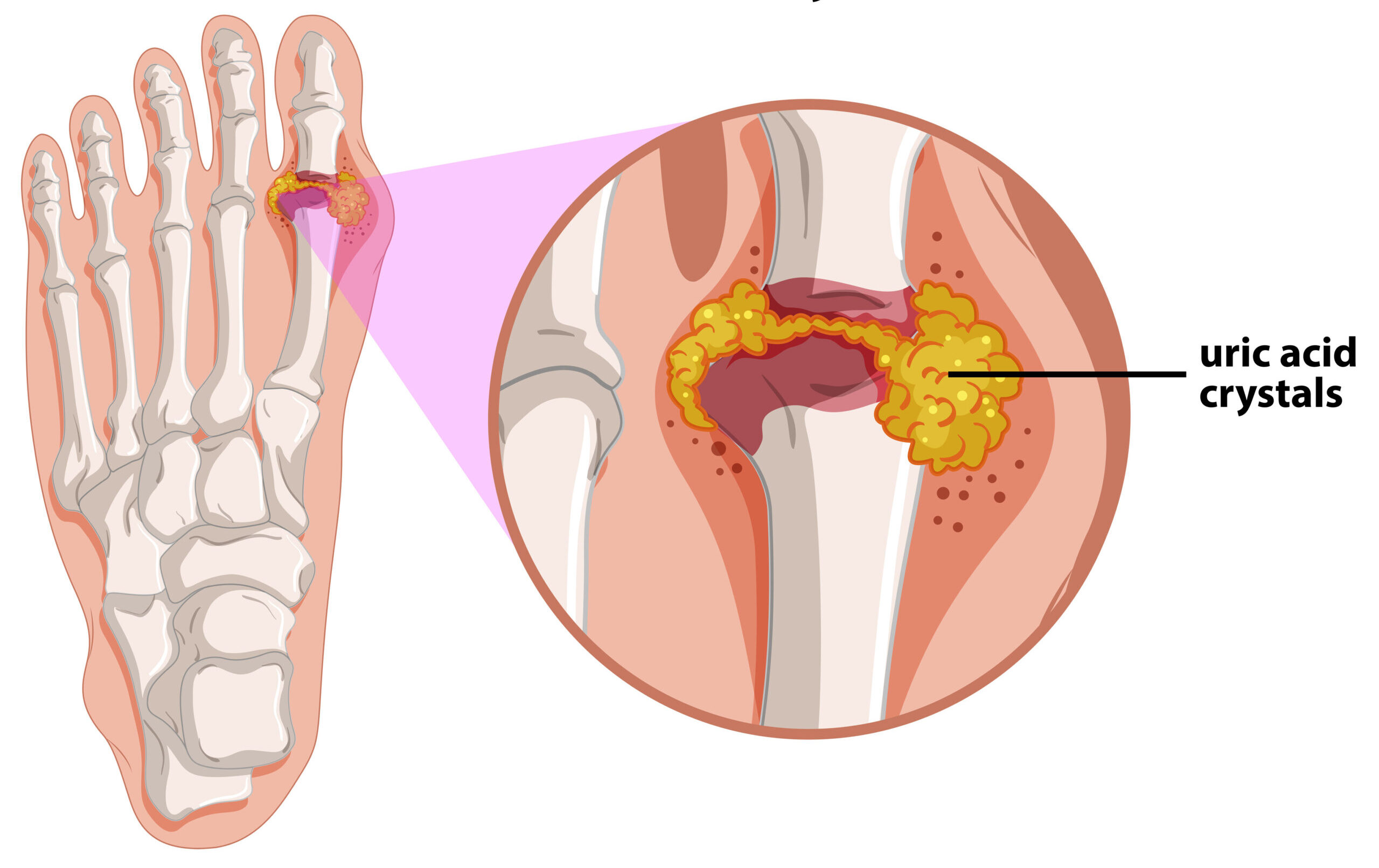
Gout, on the other hand, is a painful inflammatory condition, that is caused by a build-up of uric acid in the body which can often cause formation of gout crystal deposits on joints.
This can cause pain, swelling, and redness in several joints, including the big toe joint.
Gout affects the big toe in the majority of cases.
Key Points
Sesamoiditis and gout are two conditions that can cause pain in the big toe.
Sesamoiditis is caused by overuse or injury to the sesamoid bones, while gout is usually due to Uric acid accumulating in a certain part of the body.
- It is important to seek medical attention if you are experiencing foot pain, as proper diagnosis and treatment are essential for managing these conditions.
Understanding Sesamoiditis
Sesamoiditis is a condition that affects the sesamoid bones in the foot. These are two small bones located beneath the big toe joint, which help to absorb shock and provide leverage to the big toe during certain foot movements.
Sesamoiditis is characterized by inflammation and pain in the sesamoid bones and surrounding tissues. It is a common condition among athletes and dancers who frequently place stress on their feet and big toe in particular.
Anatomy of Sesamoid Bones
The Sesamoid bones are unique because they are not connected to other bones in the body. Instead, they are embedded in tendons and muscles.
There are two sesamoid bones located under the big toe joint: the tibial sesamoid and the fibular sesamoid.
The tibial sesamoid is located on the inside of the big toe (just under it), while the fibular sesamoid bone is located on the outer inner side of the big toe.
The sesamoid bones play an important role in the foot’s biomechanics. They help to distribute weight evenly across the foot and provide leverage to the big toe especially during pivoting movements.
Sesamoiditis occurs when there is inflammation around the sesamoid bones.
This inflammation can be caused by overuse, injury, or certain medical conditions.
Symptoms of Sesamoiditis include pain, swelling, and difficulty bending the big toe.
Understanding Gout
Gout is a type of arthritis that can cause sudden and severe joint pain. Usually, it affects the big toe, but it can also affect other joints in the feet, hands, wrists, elbows, or knees.
Gout occurs when there is a buildup of uric acid in the blood, leading to the formation of sharp crystals in the joints. This can cause inflammation, swelling, and extreme pain in the affected joint.
Some people are more likely to develop gout than others. Risk factors include being male, having a family history of gout, being overweight, drinking alcohol, having high blood pressure and consuming a high purine diet.
Which foods contain Purines?
Fish, Seafood, Haddock and meats such as bacon and liver. Sugary soft drinks which contain fructose can also cause Gout.
Symptoms of gout can include sudden and severe pain, redness, swelling and heat in the joint.
Gout attacks can last for several days or even weeks, and they can be very debilitating.
Treatment of gout usually involves the patient taking medications to reduce inflammation and help with pain relief, as well as lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of future attacks.
This may include changes to the diet, weight loss, and reducing alcohol consumption.
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of gout, as sometimes it may lead to joint damage and other debilitating issues if left unseen.
Diagnosis and Imaging Techniques
Diagnosis of Sesamoiditis and Gout involves a combination of methods, including discussing medical history and symptoms , physical examination, imaging (such as Ultrasound Scanning, MRI or X-ray), and lab testing to rule out other conditions.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests play a crucial role in the diagnosis of sesamoiditis and gout. Techniques that are commonly used in the imaging of gout include X-ray and ultrasound
X-ray is a widely used imaging technique to diagnose sesamoiditis. It can detect the presence of a fracture or any other abnormalities in the sesamoid bones.
X-rays can also help differentiate between sesamoiditis and gout. In gout, X-rays can be used to identify whether uric acid crystals are present in joints.
Ultrasound is another non-invasive imaging test that can help diagnose sesamoiditis and gout.
It can detect inflammation, fluid accumulation, and soft tissue damage.
Ultrasound is more sensitive than x-ray in detecting gout and radiologists or sonographers often look for the ‘double contour’ sign on ultrasound scan which is characteristic of gout.
Risk Factors and Causes
Sesamoiditis and Gout have different underlying causes and risk factors. Understanding these can help prevent and manage these conditions.
Lifestyle and Occupation
Certain lifestyle factors can increase the risk of sesamoiditis and gout. These include:
Overuse: Repeated stress on the foot can cause sesamoiditis. This is common in dancers, runners, and athletes. Sesamoiditis is very common in Ballet Dancers.
High-heeled shoes: Wearing high-heeled shoes can increase the pressure on the ball of the foot, leading to Sesamoiditis.
Trauma: A direct injury to the foot can cause sesamoiditis or gout.
- Obesity: Being overweight can increase the risk of developing gout.
Occupational factors can also play a role in the development of these conditions. For example, jobs that require standing for long periods of time can increase the risk of developing sesamoiditis.
Some other risk factors for gout include:
Age and gender: Gout is more common in men over the age of 30.
Genetics: A family history of gout can increase the risk of developing the condition.
Hypertension: High blood pressure can increase the risk of developing gout.
Diuretics: Certain medications, such as diuretics including Furosemide, can increase the risk of gout.
- Diet: Eating a diet high in purines, such as red meat and seafood, can increase the risk of gout.
It is important to note that not everyone with these risk factors will develop sesamoiditis or gout.
However, being aware of these risk factors and making lifestyle changes where possible can help reduce the risk of developing Gout.
Treatment and Management
Medication and Therapy
Treatment for sesamoiditis or gout often involves a combination of medication and therapy.
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen may be recommended to relieve pain and inflammation.
In suspected cases of gout, stronger prescription medications, such as Corticosteroids or Colchicine may be prescribed.
Both conditions often respond to a Cortisone injection into the big toe.
In severe cases of chronic sesamoiditis, surgery may be a last resort if other methods are not working.
Footwear and Orthotics
For Sesamoiditis, Gel pads or tailor made orthotics made by Podiatrists may help reduce the pressure on the underside of the big toe and help relieve the pain.
Footwear and orthotics are a great way to help in preventing and managing sesamoiditis and gout.
Shoes with a wide toe box and good arch support can help reduce pressure on the foot and prevent irritation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes of pain in the ball of the foot?
Pain in the ball of the foot can be caused by a variety of conditions, including Sesamoiditis and Gout. Other common causes of pain in the ball of the foot include Osteoarthritis, Turf Toe (injury to the plantar plate) and stress fractures.
How can sesamoiditis be treated?
Sesamoiditis can be treated with rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medication. In some cases, a doctor may recommend immobilization with a cast or walking boot or steroid injections.
Orthotics or shoe inserts can also be helpful in reducing pressure on the sesamoid bones. In severe cases, surgical treatment may be necessary.
What are the symptoms of Sesamoiditis?
The most common symptom of sesamoiditis is pain in the ball of the foot, particularly under the big toe. The pain may be sharp or dull and may worsen when walking or running. Other symptoms may include swelling, bruising, and difficulty bending the big toe.
Are orthotics helpful in treating sesamoiditis?
Orthotics or shoe inserts can be helpful in reducing pressure on the Sesamoid bones and relieving pain. A doctor may recommend custom orthotics or over-the-counter inserts to help support the foot and reduce stress on the Sesamoid bones.
Can Sesamoiditis be mistaken for other foot conditions?
Sesamoiditis can be mistaken for other foot conditions, such as Gout or Osteoarthritis of the big Toe. At MyMSK Clinic the doctor will usually perform a physical examination and often perform an Ultrasound Scan to confirm a diagnosis.
Is Sesamoiditis related to plantar fasciitis?
Sesamoiditis is not directly related to plantar fasciitis.
Plantar fasciitis occurs near to the heel whereas sesamoiditis occurs under the big toe.
Do Injections Treat Sesamoiditis or Gout?
Yes. Both conditions often respond to a Cortisone injection into the big toe. This procedure can be done at our clinic in Manchester.
First we often perform a examination on the area which may involve an ultrasound scan.
The Doctor the suggests the best cousre of treatment suited to you.
To Arrange a consultation in Manchester or Burnley visit our online Booking Page or call us on 0333 772 9655.

